
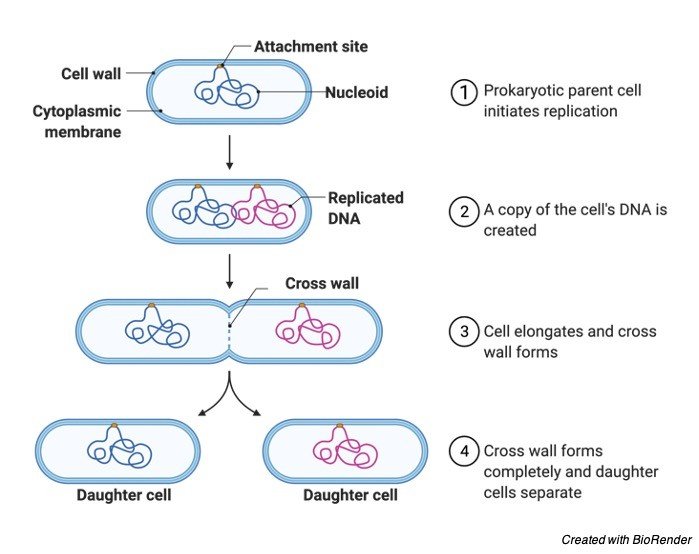
The replicated chromosomes then separate, forming two identical sets of genetic material.Ĭell Division: Once the nucleus has divided, the cell undergoes cytoplasmic division. Nucleus Division: Amoeba has a single nucleus, which replicates its genetic material through DNA synthesis. It takes in nutrients and energy from its environment to support the upcoming division process. Here’s a brief description of binary fission in AmoebaĬell Growth: During binary fission in Amoeba, the parent cell undergoes a period of growth and nourishment to prepare for reproduction. However, the lack of genetic diversity resulting from this method of reproduction can limit bacterial adaptation to changing environments and make them susceptible to environmental challenges and the effects of mutations.īiology Articles Asexual Reproduction Fragmentation How do Organisms Reproduce Binary fission in Amoebaīinary fission is a common mode of reproduction in Amoeba, a single-celled organism belonging to the group of protozoans. Since the daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell, binary fission maintains the genetic continuity of the bacterial population. Each daughter cell obtains a copy of the replicated DNA and other cellular components.Ĭompletion: Once the septum is fully formed, the two daughter cells are released, becoming independent bacterial cells capable of their own growth and reproduction.īinary fission in bacteria is a rapid and efficient process, allowing for exponential population growth. This septum grows inward, eventually dividing the cell into two separate compartments.Ĭell Division: The septum continues to grow until it completely separates the two daughter cells. Septum Formation: As the cell elongates, a septum, or a partition, starts forming at the midpoint of the cell. The cell wall and membrane components also increase to accommodate the division process. The circular DNA molecule present in the cell is duplicated, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material.Ĭell Elongation: Following DNA replication, the bacterial cell elongates as it prepares for division. Replication: Before binary fission, the bacterial cell undergoes replication of its genetic material. Here’s a brief description of binary fission in bacteria It is a process by which a single bacterial cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Binary fission in Bacteriaīinary fission is the primary method of reproduction in bacteria. However, binary fission results in limited genetic diversity, which can limit the ability to adapt to changing conditions and makes populations susceptible to environmental challenges and the spread of harmful mutations. This form of reproduction is advantageous for single-celled organisms living in favorable environments, as it allows for rapid multiplication and colonization.
EXAMPLE OF BINARY FISSION FULL
The genetic material is replicated and distributed equally, ensuring that each daughter cell inherits the full complement of genes from the parent cell. It does not involve the formation of specialized reproductive structures or the fusion of gametes. In binary fission, the entire process, from replication to cell division, is usually relatively quick and efficient. Binary fission allows for rapid population growth and the production of genetically identical offspring, ensuring the propagation of successful traits in stable environments. The division occurs through the constriction of the cell membrane and the synthesis of a new cell wall or membrane between the two daughter cells.


Each daughter cell receives a copy of the parent’s genetic material, ensuring genetic continuity. During binary fission, the parent cell undergoes replication of its genetic material, followed by division of the cell into two equal parts. It is a process by which a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells.

The parent cell duplicates its genetic material and then divides into two identical daughter cells.īinary fission is a form of asexual reproduction commonly observed in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and some protists. This method is commonly observed in single-celled organisms such as bacteria and protists. Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
